Regulations of Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in Kuwait
Eng.Manal AL-Saleh
The Current situation of waste water in Kuwait
* Kuwait is classified as one of the best countries in the world in the infrastructure with regard to the sewage system.
* Kuwait has a national sewage network which is estimated at 800 linear km.
* The sewage waste water is transmit from 98% of the facilities in the country.
* The country suffers from the 2% remaining waste water which represent both sewage and industrial waste water from areas not covered by public network, and was disposed in the landfill sites .
Quantities ... Type … and sources
* The Estimated daily quantities of the remaining waste water is about 4-5 million gallons per day (about 23 thousand cubic meters / day).
* This waste is produced from many development facilities, such as industrial areas, slaughterhouses, boarder stations, military camps and oil activities.
Transportation
* The Country suffers from uncontrolled transportation of the waste water.
Disposal
* For more than four decades the disposal of sewage and industrial waste water was continued to improper landfill sites.
First : Solutions for transported sewage waste water by tankers : 
Um Al-Haiman Landscaping project
The treated sewage from Um Al-Haiman treatment plant is used to the landscaping project for Um Al-Haiman area in order to improve air quality.
The pilot plant for sewage treatment using plants (Wetland)
* A tri Committee represented from Environment Public Authority ,KM and Security Committee to follow up decisions of the Council of Ministers has implemented a sewage treatment station using natural process , aggregate and gravel which is located in Jeleeb Camp.
* The plant has been designed to receive sewage waste water for about 600 people.
* The treated waste water meets the standards and requirements for each of the K- EPA and the MPW. 
Second :Industrial Waste Water transported by tankers :
Challenges
* The absence of laws and requirements of the carriers in terms of security, safety and environment.
* A Long period of time is required for commitment of all the sources to install treatment units.
* The fear of affecting the pumping stations of MPW when the ministry deliver the treated water at the source from industrial areas especially in case of un treated industrial waste water whether it was intentional or unintentional.
* Severe effect on soil and groundwater at disposal sites.
Industrial Waste Water transported by tankers:
Solutions
Adoption of strategic solution as follows:
* build a treatment plant for industrial waste water to accommodate all amounts of waste disposed in landfills (for short term).
* The treatment plant which is considered as an emergency plant receives all amounts of liquid waste from variable sources (such as construction projects) and stationary sources (factories in case of maintenance - plants with small amounts of waste water , which do not require installation of treatment units).
* All sources are committed to install treatment units at the source for their industrial waste water.
* Establishment of sub-stations in all industrial areas receiving treated water from sources to ensure the safety for the MPW stations.
The proposed strategy for handling industrial effluents
|
Treatment in the source (Primary treatment) Each manufacturing facility should treat the waste at the source according to PAI decision No. 15/2007 |
| The result water from the pre-treatment unit have a similar in characteristics and components with sewage and its allow to be send to the proposed substations |
| Ensure that primary treatment is not affected by biological treatment in the proposed sub-stations in the second stage |
|
Sub-stations (tertiary treatment) These stations established at the end of sewer lines in all industrial area |
| These stations contribute to the treatment of sewage from industrial plants also the primary treated waste in the source |
| The existence of these stations will ensures that MPW pumping stations and treatment plants will not be affected, especially in the event of non-legal connection to the public network or in the event of failure of treatment in the source |
|
Central station for treating Liquid industrial waste Stop the random landfill extends for more than 40 years |
| Build a central station to receive all amounts all the waste until the completion of the installation pre-treatment units at source |
| Completion of the infrastructure of the PAI and enable them to treat liquid industrial waste in addition to the Shuaiba disposal of industrial solid waste plant |
Rehabilitation of Wafra K-14 waste water landfill site 
* The Tri Committee immediately started rehabilitation of the wastewater landfill site after it was closed.
* It took one year of extensive efforts under the scientific super vision of KU.
* It is planned to convert the site into recreational area.
Achievements
1. Treatment at the source: The committee succeeded in coordination with the PAI, which issued the decision No. 15/2007 obliging all industries to install a treatment unit at the source.
2. Sub-stations: Installing sub-stations in all industrial areas in Kuwait.
3. Building up Industrial waste water treatment plant.
Wafra K-30 Industrial Treatment Plant 
* The plant consists of three phases:
1. First phase (Receiving lagoons) There are three major lagoons (for food industry - high content of oils - others) in addition there is a receiving unit for waste water with a high content of trace metals.
2. Second phase(pre treatment) Consist of :
* Oil and sand Trap.
* Chemical dosing.
* Flotation system.
3.Third phase :
* The biological treatment and it can accommodate 20,000 m3/day. 
* The sludge generated from the process is taken to an incinerator for thermal destruction in a safe and environmentally sound way.
* Landscaping Wafra Industrial Treatment Plant
* Treated water is stored in tanks of a total capacity of 13,000 m3, after which the entire area of 250,000 m2 is irrigated.
The usage of Treated water
* Because the treated water specification is in compliance with article no. 61 from decision no. 210/2001 (Treated liquid wastewater must not exceed limits allowed listed in Appendix (15) of this regulation when used for irrigation). 
* The main usage of the treated water from both Um-Al-Haiman and Al-Wafra treatment plants is used for irrigation.

The Guideline and specification for treated waste water
Chapter V of decision no. 210/2001 “PROTECTION OF MARINE AND COASTAL ENVIRONMENT”
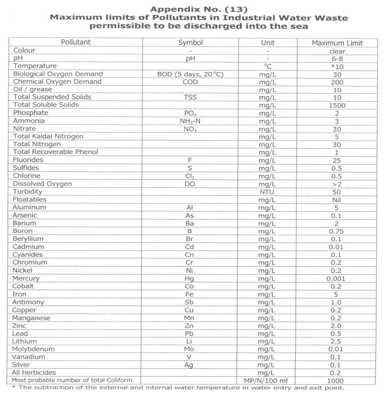
* (ARTICLE 59): Liquid-Effluent discharge into the marine environment should not exceed levels listed in Appendix (13) of this regulation. In any case, it is not allowed to discharge treated liquid waste in the marine environment except at a distance no less than 500 meters from the coast. Liquid effluent should not be discharged in fishing areas, swimming areas and natural sanctuaries.
* (ARTICLE 60): Industrial liquid discharge into public drains should not exceed allowed limits listed in Appendix (14).
* (ARTICLE 61): Treated liquid waste water must not exceed limits allowed listed in Appendix (15) of this regulation when used for irrigation.



Satellite image

Reference:
Proceeding of the Workshop on "Appropriate Wastewater Reclamation and Reuse Technologies for Arid Environments"








